The Middle East has been lately a bed of discoveries and the excavations are earning us some interesting pieces of history. Recent excavation by DCT Abu Dhabi for roads led to the discovery of artefacts belonging to the pre-islamic era. It’s safe to say that the discovered artefacts would date from 1300 BCE to 600 CE span. What are these artefacts and what’s the history attached to them?
DCT Abu Dhabi Excavations Led To Artefacts Discoveries
We have made several significant new archaeological discoveries in the emirate, including sites and artefacts from the Iron Age (1300-300 BCE) and the Late Pre-Islamic period (300 BCE-400 CE).
To learn more about the significant finds #InAbuDhabi, visit: https://t.co/r4T5jAAlFn pic.twitter.com/Hm6q7IROYM
— Department of Culture and Tourism – Abu Dhabi (@dctabudhabi) June 16, 2023
In Al Ain, the Department of Culture and Tourism (DCT) Abu Dhabi has discovered new locations and artefacts that date back to the Iron Age and the Pre-Islamic period. A pre-Islamic cemetery was found in the Kuwaitat suburb of Downtown Al Ain as a result of road and infrastructure reconstruction, prompting DCT Abu Dhabi to conduct excavations. In an effort to learn more about UAE history and preserve its cultural legacy, DCT Abu Dhabi is conducting excavations and research.
Also Read: Skip Delivery, Try Careem’s ‘DineOut’ That Offers Discount On Dining In Dubai
List Of Items Discovered
“The exciting archaeological discoveries in Al Ain are the result of ongoing efforts to uncover and protect the rich history of the emirate and the wider nation. DCT Abu Dhabi is making significant contributions to knowledge about life in the region during time periods pic.twitter.com/LTDCRPLUez
— Department of Culture and Tourism – Abu Dhabi (@dctabudhabi) June 16, 2023
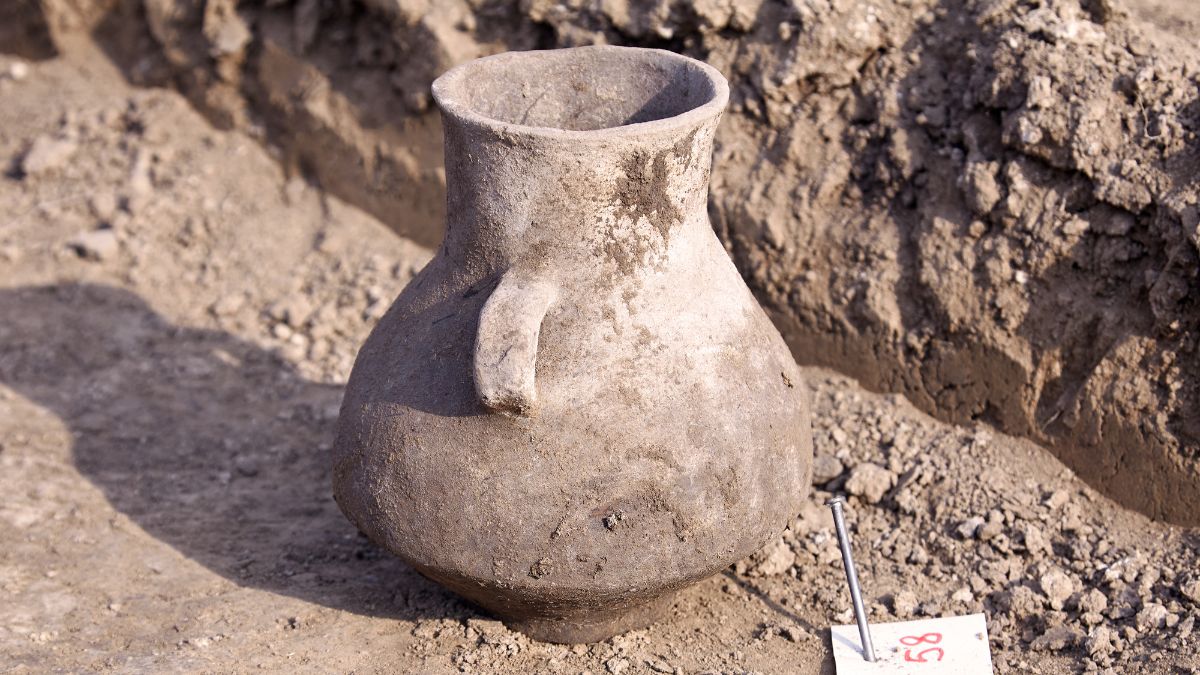
Twenty distinct graves with some incredibly well-preserved objects were discovered during the excavation effort. Ceramic, copper, glass, and alabaster artefacts are among the items discovered. The burials also contained a sizable collection of undamaged iron weapons, such as arrows, spears, and swords.
Along an 11.5km span that encompasses three regions in Al Ain, including another cemetery and the Khrais, Qattara, and Hili neighbourhoods, DCT Abu Dhabi has discovered other gems. In addition to at least 35 tombs, the cemetery is from the Iron Age and features a colossal stone tomb.
In addition, DCT Abu Dhabi discovered more than 50 ancient aflaj, or water channels, which are signs of agriculture. These canals used various building methods and originated from various eras. This demonstrated that there was agricultural activity in the area during several periods of the Iron Age. It also illuminates the many prehistoric irrigation techniques and farming methods applied in this area.
The department thinks that the pottery and other items found in the graves were utilised in agricultural and burial rituals. Items including soft stone pots, jewels, shells, metals, and weapons can be found in these ornaments. Additionally, soil samples were taken from the location, which will provide more information about the types of crops produced there at the time.
What do you think were these items utilised for in the early ages?
Cover Image Courtesy: Canva Stock Images
First Published: June 18, 2023 7:26 PM