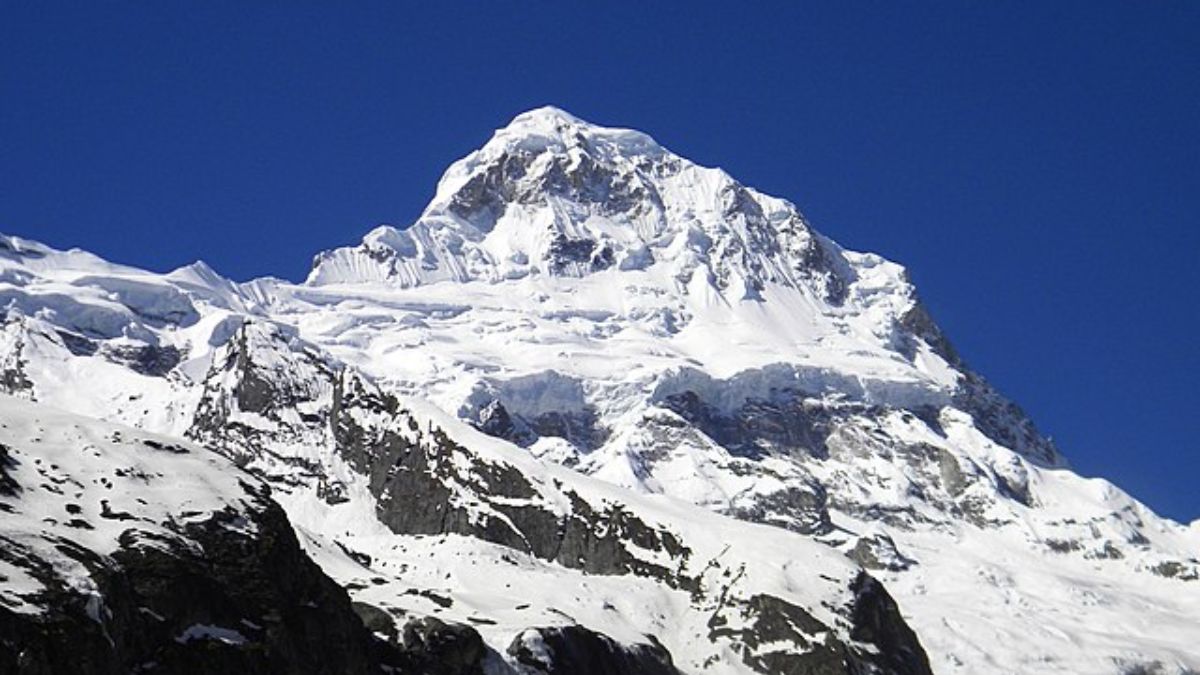
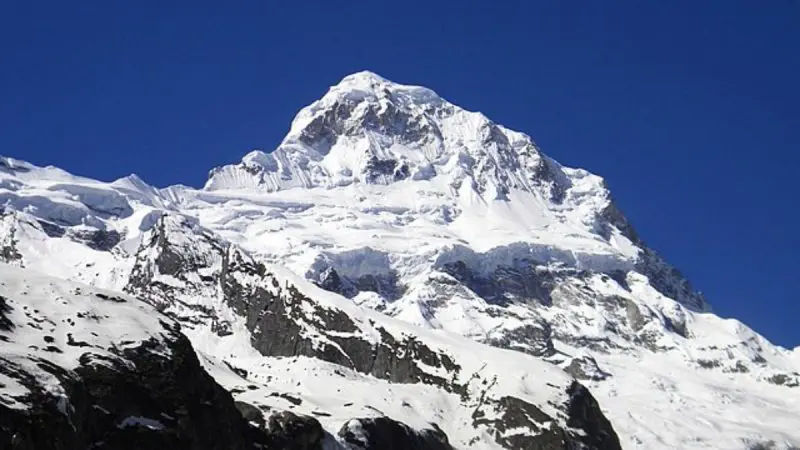
According to a study, the glacier area of Uttarakhand shrank from 979 square kilometres in 2000 to 957.6 square kilometres in 2023, with an average yearly deglaciation rate of 0.095%. According to the research, the main causes of this notable retreat in Uttarakhand glaciers are air pollution, climate change, and rising temperatures.
The Study on Uttarakhand Glaciers

The study, which examined 116 glaciers in the state over a 23-year period and was published in the peer-reviewed journal ‘Earth Surface Processes and Landforms’, discovered that the region’s total glacier area has been shrinking at an average annual deglaciation rate of 0.095%.
According to the study, Gangotri Glacier recorded the highest area loss, shrinking by 2.38 sq km, followed by Panpatia Glacier, which lost 2.18 sq km. The study was titled ‘Glacier area variation in Uttarakhand Himalaya: Investigating trends and influencing factors.’ G27, a smaller glacier, experienced the quickest rate of retreat, shrinking. It went from 0.595 sq km in 2000 to 0.401 sq km in 2023, with an annual reduction rate of 1.41%.
Why Is The Glacier Sinking?
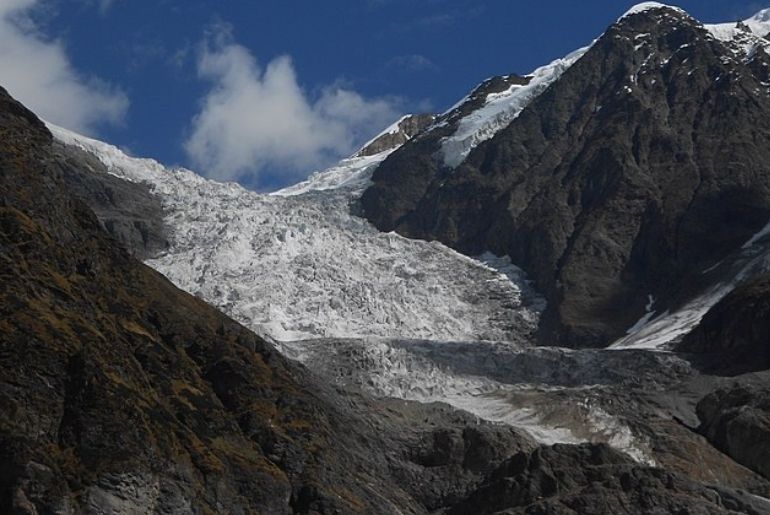

Iti Shrivas, Supratim Guha, Reet Kamal Tiwari, Mohit Prajapati, and Ashutosh Laxman Taral are the authors of the study. The study mapped 979 square kilometres of glacier area or around 39% of Uttarakhand’s glaciated territory. The size of the glaciers under analysis ranges from 0.36 to 118.3 square kilometres.
It found that the main cause of glacier retreat was climate change and that the Himalayas were more severely affected than the rest of the world. The main causes of glacier melt were found to be changing precipitation patterns, air pollution, especially from black carbon accumulation, and rising temperatures.
According to the study, topography, slope, debris cover, and shape index are some of the variables that affect glacier retreat, which is not constant. The form index, which gauges how long or compact a glacier is, is one of the most important factors found. A 10% increase in shape index reduces glacier loss by 0.112% annually, suggesting that elongated glaciers with a higher shape index are more stable than compact, circular ones.
According to the experts, the slope is also very important, with steeper glaciers losing less land than those with gentler slopes. Because steeper topography allows for faster ice movement, which reduces extended exposure to higher temperatures, it was discovered that glaciers lost 0.11% less area annually for every 10% increase in slope.
Cover Image Credits: Wikimedia Commons
For more such snackable content, interesting discoveries and the latest updates on food, travel and experiences in your city, download the Curly Tales App. Download HERE. First Published: February 14, 2025 7:14 PM