Advancements in technology have revolutionized various industries, and the culinary world is no exception. Among the fascinating innovations, 3D-printed food stands out as a unique concept that combines cutting-edge technology with culinary arts. But, what implications does it have on the future of food production?
The Process Of 3D-Printed Food
Dinner guests love our dessert London After Eight: 3D-printed lemon cream with exquisite chocolates from @Valrhona! pic.twitter.com/s6SXuq5mTh
— Food Ink (@FoodInk3D) August 2, 2016
While 3D-printed food is still considered a niche concept, it has found applications in various areas. With the ability to create custom-designed food items, 3D printing allows for precise control over ingredients, portion sizes, and nutritional content.
In reality, 3D-printed food is still in its infancy and has a long way to go before seeing a broader adoption from professionals and consumers. The foods that can be 3D printed are limited to the processes available. While still in its early stages, it has already showcased its potential in personalized nutrition, food customization, and sustainable food production.
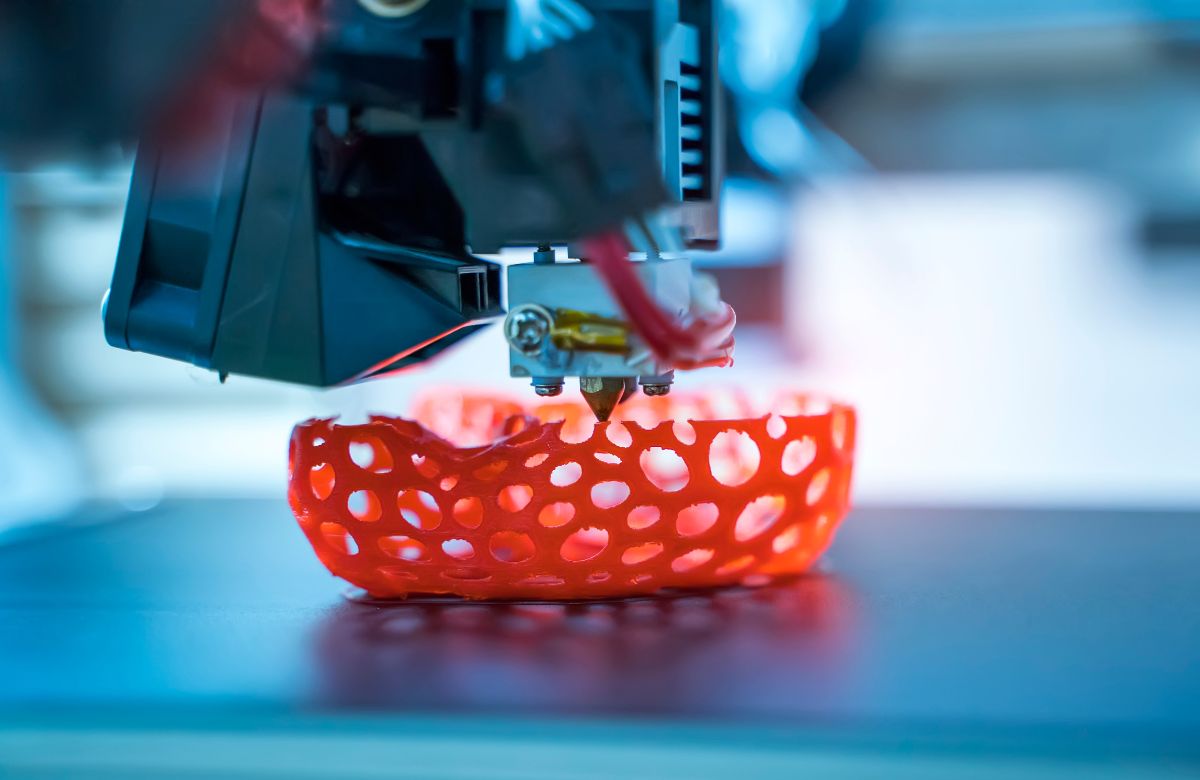
Food 3D printers are best to create complex forms and patterns rather than cooking the contents. Once the edibles have been 3D printed, they are often either ready to eat or will be cooked thereafter.
Also Read: 3D Printed Walls To Plastic-Free Shopping: Visit This Exhibition At The Museum Of The Future
How Is 3D-Food Printing Done?
#FoodInk 's pop-up in pop-art! We love @BedourAldakhil 's photo collage of our #3D printed food
https://t.co/rKwLS4iDdA— Food Ink (@FoodInk3D) July 21, 2016
The process of 3D-printed food involves several steps, starting from ingredient selection to the final production of the edible masterpiece. The first step is choosing the appropriate ingredients, which can range from semi-liquid doughs and purees to gels and chocolates. At first, it might feel a bit restricted in terms of options but think of all the possible combinations between doughs, mashes, cheeses, frostings, and more.
Once the ingredients are ready, a digital model or design is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This determines the shape, texture, and overall appearance of the food item. The digital design is then loaded into the 3D printer, which follows the design and deposits the food material layer by layer.
The printer’s extrusion system pushes the material through a fine nozzle. Additionally, this helps to gain precise control over the shape and placement of the food. After the printing process is complete, additional steps such as cooling, baking, or post-processing techniques may be employed. This helps to enhance taste, texture, or appearance.
While there has been significant interest and experimentation, it has not yet become mainstream.
Cover image credits: Canva
First Published: June 30, 2023 5:58 PM