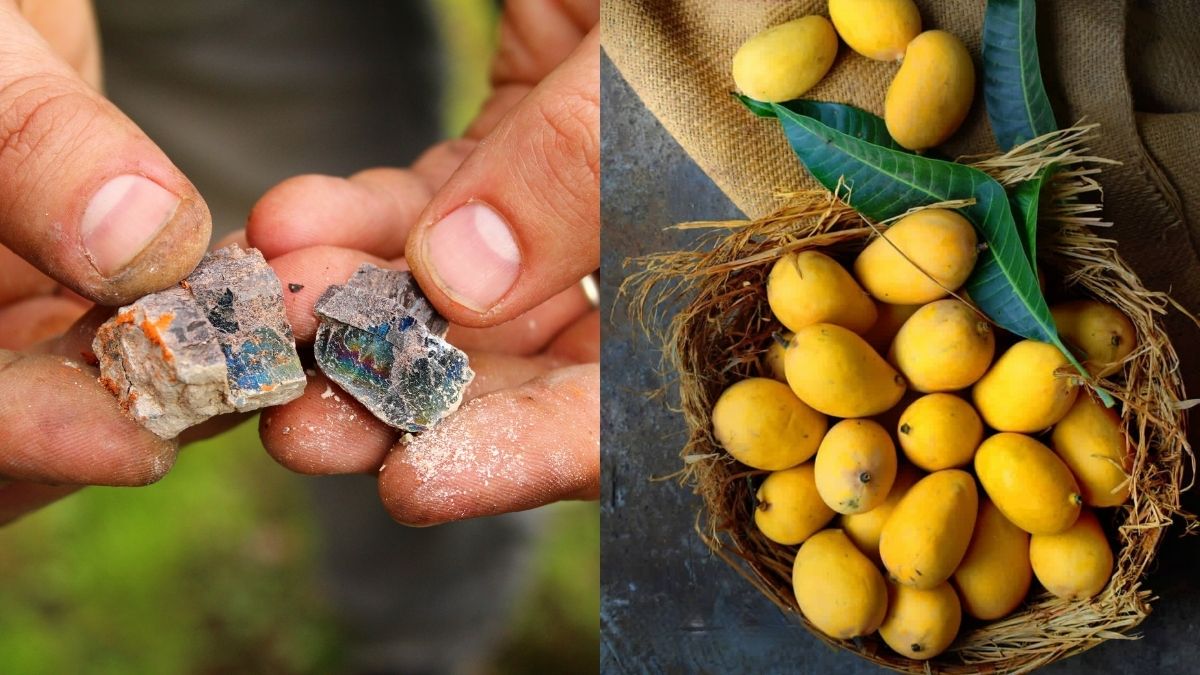
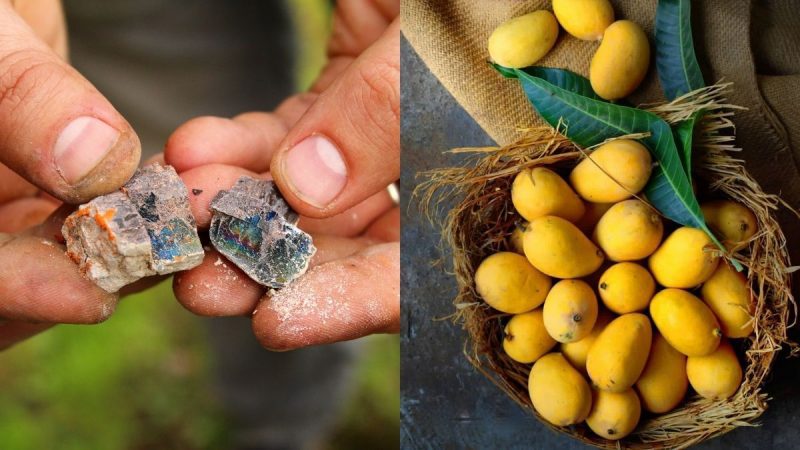
The Food Safety And Standards Authority Of India or FSSAI recently issued an alert to traders, fruit handlers and business operators alike. The alert was against the use of calcium carbide or carbide gas which is commonly used for the ripening of fruits. The FSSAI has warned against its use and said that strict action will be taken against those who are found to be violating this rule. But why is calcium carbide or carbide gas prohibited by FSSAI?
Why Is Calcium Carbide Prohibited By The FSSAI For Fruits?
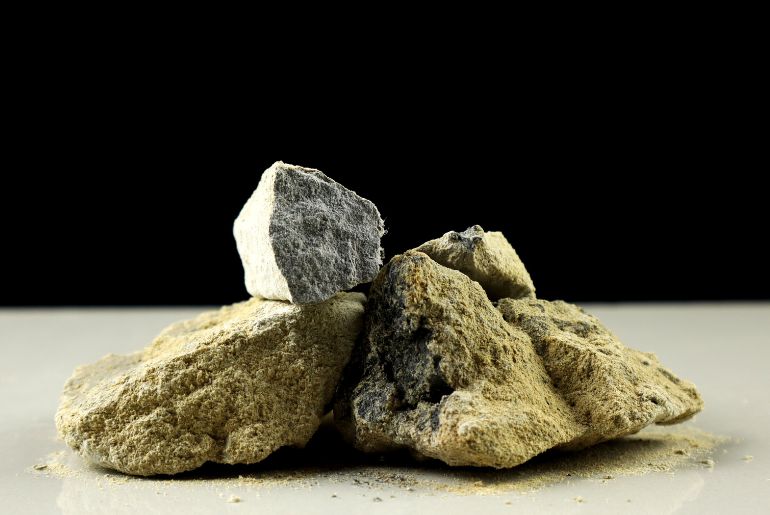

According to an article which was recently published by NDTV, this particular chemical can cause a lot of adverse effects on humans. It releases a gas called acetylene that contains phosphorous as well as arsenic.
Consuming these substances can cause irritation, dizziness, excessive thirst, vomiting, skin ulcers and even difficulty in swallowing. As per regulation 2.3.5 of Food Safety and Standards, 2011, the use of acetylene or carbide is prohibited for the purpose of artificially ripening fruits.
This reminder comes amid the peak of mango season. Mango is a widely loved seasonal fruit and because of high demand, many fruit handlers and businesses might be tempted to use the chemical to harvest large quantities of the fruit to sell in the market. Staying vigilant is, therefore, crucial.
Also Read: 5 Sure-Shot Ways To Find Out If Your Mangoes Were Artificially Ripened!
What Other Alternatives Are They Allowed To Use, If Any?

Instead of acetylene gas, the FSSAI has allowed the use of ethylene gas for the purposes of ripening fruits and vegetables. It is deemed to be safer than carbide as it promotes the natural process of ripening fruit.
Ethylene is also a hormone present naturally in fruits. It therefore acts as a catalyst for the entire process rather than bringing it on artificially. There are, however, limits to the amount of ethylene that can be used.
As per the NDTV article, only 100 ppm or parts per million of ethylene will be permitted depending on the size, maturity and type of the fruit.
Also Read: Neotame, An Artificial Sweetener Found In Cakes & Soft Drinks, Can Cause Gut Damage: Study
Do you have hacks for spotting fruits that have been ripened via harmful chemicals? Let us know in the comments section below!
Cover Image Credits: Canva Images
For more such snackable content, interesting discoveries and the latest updates on food, travel and experiences in your city, download the Curly Tales App. Download HERE.
First Published: May 20, 2024 1:39 PM