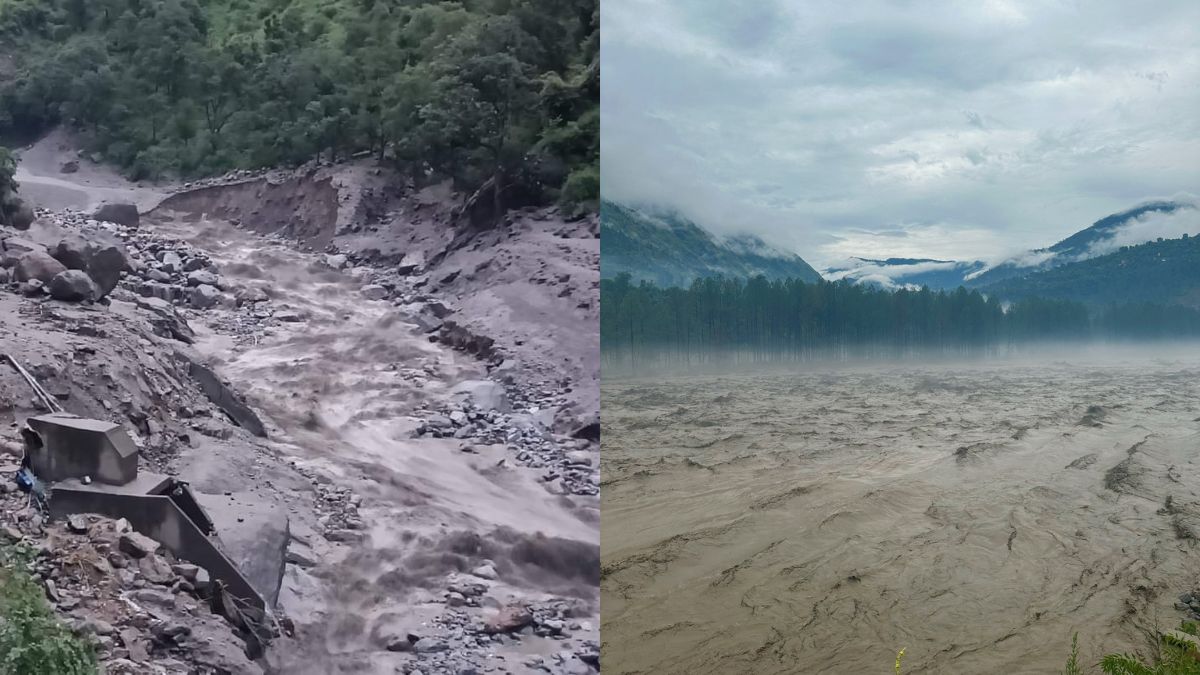
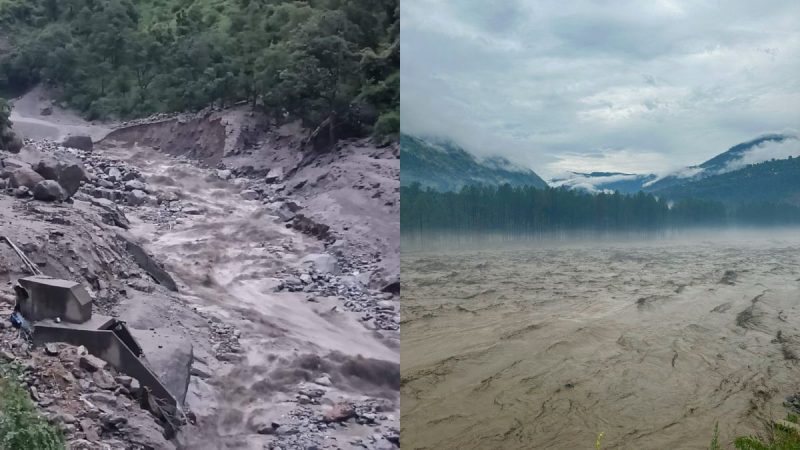
Extreme rainfall devastated Himachal Pradesh on July 31, 2024, causing widespread destruction. A report by the non-profit Himalaya Niti Abhiyan (HNA) has linked this catastrophe to global warming, emphasising the increasing risks posed by changing climate patterns in the region. The report specifically focuses on the devastation in Himachal Pradesh, where heavy rains and cloudbursts have become more frequent due to climate change.
Cloudbursts In Himachal Pradesh
देवभूमि हिमाचल प्रदेश के कुल्लू,मंडी,शिमला में बादल फटने और भारी वर्षा से हुए जानमाल नुकसान से कई परिवारों ने अपनो को खोया है,यह समाचार अत्यंत दुखद है।#CloudBurst हिमाचल प्रदेश#HimachalPradesh pic.twitter.com/T5qi00bylc
— Annu (@HinduChhori) August 1, 2024
The warming of the Himalayan region is almost twice as fast as other parts of the world, according to multiple studies cited in the report. This accelerated warming has led to a higher frequency of destructive incidents. This is particularly due to the collision of the southwest monsoon and western disturbances. These climatic shifts have made the Trans and High Himalayas more susceptible to disasters.
The report highlights that melting glaciers in the region have left behind large amounts of loose sediments, which are easily washed away by sudden heavy rains. This sediment poses significant threats to hydropower projects and infrastructure.
A fact-finding report was compiled by HNA and submitted to the state government. It highlighted that the bursting of the Malana hydro dam due to a flash flood on August 1 once again demonstrated the significant threat dams pose to life and property. The report noted that “no lessons have been learnt by dam authorities.”
Solutions To Prevent Climate Change-Induced Cloudbursts
Recently, parts of #Himachal has been the epicentre of a terrible #cloudburst. Shrikhand Mahadev area near Nirmand and surrounding Nalas have witnessed loss of multiple lives property. In the midst of the disaster let’s appreciate the efforts of the first responders. pic.twitter.com/PnSsPLNbq5
— Dr. Karthikeyan Gokulachandran, IPS (@karthikeyangips) August 3, 2024
In response to these growing threats, the HNA report offers several key solutions to prevent and mitigate the impacts of climate change-induced cloudbursts. One of the primary recommendations is to halt large hydroelectric projects in high-risk areas. This can destabilise the environment and increase the likelihood of cloudbursts and landslides. The report also calls for the creation of separate plans and guidelines for construction and development in paraglacial areas, where the risks are especially high.
Another critical recommendation is to stop major development activities, such as large-scale construction, in areas above 8,000 feet. This is because the fragile ecosystem is more prone to the impacts of climate change.
The report strongly recommends installing early warning systems to provide timely alerts about approaching extreme weather conditions. Additionally, the report advises limiting the use of blast and drill methods for building and widening roads. They suggested that the Cut-and-Fill method, though more expensive, should be adopted instead to minimise environmental disruption.
Also Read: Kullu-Manali Highway Partially Restored For Vehicular Traffic Following Catastrophic Cloudburst
HNA team members attributed the increasing high-intensity rainfall and flash floods to global climate change and receding glaciers. These have loosened the soil, leading to landslides. The team also noted that human activity, such as the construction of hydroelectric projects and roads in sensitive areas, has exacerbated the impact of these natural disasters.
Cover Image Courtesy:@theEcoglobal,@HinduChhori/X (Formerly, Twitter)
For more such snackable content, interesting discoveries and the latest updates on food, travel and experiences in your city, download the Curly Tales App. Download HERE. First Published: August 09, 2024 1:28 PM